Blockchain technology has transformed various industries, with financial services being one of the key sectors experiencing significant disruption. The ability of blockchain to provide transparency, security, and decentralization has made it an attractive solution for managing financial transactions. However, not all blockchains are created equal, and choosing the most secure blockchain for financial transactions is critical. In this article, we will explore the different types of blockchains and their security features, helping businesses and individuals select the best blockchain for their financial needs.
Understanding Blockchain and Financial Transactions
Before diving into the types of blockchains, it’s essential to understand how blockchain works and why it’s so secure. A blockchain is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records transactions across multiple computers in a decentralized network. Each block contains transaction data, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block, forming a chain. This design ensures that once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or tampered with, providing a high level of security for financial transactions.
Types of Blockchain for Financial Transactions
There are three main types of blockchain technologies: public blockchains, private blockchains, and consortium blockchains. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, particularly when it comes to security and financial transactions.
1. Public Blockchain
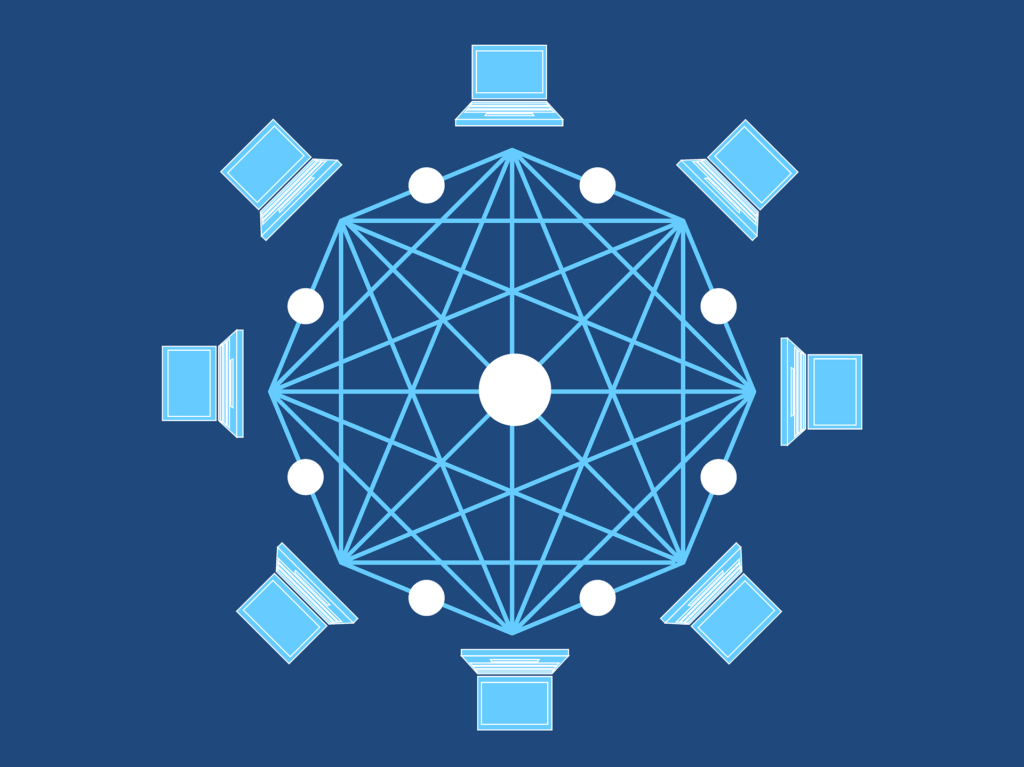

A public blockchain is open and decentralized, meaning anyone can join the network, validate transactions, and participate in the consensus mechanism. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public blockchains.
Security Features of Public Blockchains:
- Decentralization: Public blockchains are highly decentralized, reducing the risk of a single point of failure or malicious manipulation.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Public blockchains typically use consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions. These mechanisms provide robust security by requiring participants to solve complex cryptographic problems or stake assets to participate in validation.
- Transparency: Transactions on public blockchains are visible to everyone in the network, which ensures transparency and accountability.
Advantages for Financial Transactions:
- Public blockchains offer high security due to the decentralization and cryptographic validation methods.
- The transparency of the blockchain helps reduce fraud and promotes trust among participants.
Disadvantages:
- Public blockchains, particularly Bitcoin and Ethereum, can suffer from scalability issues and slower transaction speeds due to the large number of participants.
- Transaction fees can be high, especially during periods of network congestion.
2. Private Blockchain
A private blockchain is a permissioned blockchain, meaning that only authorized participants can join and validate transactions. Private blockchains are typically controlled by a single organization or consortium, providing more centralized control compared to public blockchains.
Security Features of Private Blockchains:
- Controlled Access: Only trusted participants are granted access to the network, reducing the risk of external threats or malicious actors.
- Faster Consensus Mechanisms: Private blockchains can use more efficient consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Authority (PoA), where validators are pre-approved entities.
- Privacy: Private blockchains prioritize privacy by limiting access to transaction data to only authorized parties.
Advantages for Financial Transactions:
- Private blockchains offer faster transaction speeds and lower costs because they have fewer participants.
- They provide enhanced control over the network, allowing for more stringent security protocols.
Disadvantages:
- The centralized nature of private blockchains means that a single entity controls the network, which may pose a security risk if the central authority is compromised.
- Lack of transparency may be a concern for financial transactions that require auditing or public visibility.
3. Consortium Blockchain
A consortium blockchain is a hybrid between public and private blockchains. In a consortium blockchain, multiple organizations share control over the network, but access is still permissioned. This model is often used in industries where multiple entities need to collaborate securely.
Security Features of Consortium Blockchains:
- Shared Control: Consensus is maintained by a group of pre-selected organizations, ensuring that no single entity has complete control over the network.
- Efficient Consensus Mechanisms: Consortium blockchains typically use more efficient consensus mechanisms such as Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), which is more scalable and energy-efficient than PoW or PoS.
- Enhanced Privacy and Security: As with private blockchains, consortium blockchains ensure that transaction data is only visible to authorized parties, ensuring privacy.
Advantages for Financial Transactions:
- Consortium blockchains are ideal for businesses that need to collaborate with trusted partners while maintaining security and privacy.
- These blockchains are more scalable and efficient than public blockchains, making them suitable for financial transactions with higher volumes.
Disadvantages:
- Although more decentralized than private blockchains, consortium blockchains still rely on a smaller number of validators, which could make them more vulnerable to attacks or collusion among validators.
- Governance and consensus processes can be more complex due to the involvement of multiple organizations.
Which Type of Blockchain is Most Secure for Financial Transactions?
When evaluating the most secure blockchain for financial transactions, it’s important to consider the following factors:
- Decentralization vs. Control: Public blockchains offer the highest level of decentralization, reducing the risk of manipulation. However, private and consortium blockchains provide more control over the network and allow for faster transaction speeds.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Public blockchains use PoW or PoS, both of which offer robust security. Private and consortium blockchains, with their more efficient consensus mechanisms like PoA or PBFT, may offer faster transactions but may not have the same level of decentralization.
- Privacy and Transparency: For financial transactions, privacy is crucial. Private and consortium blockchains offer more privacy by limiting access to transaction data. However, this comes at the expense of transparency.
- Scalability and Transaction Speed: If you need to process a large volume of transactions quickly, private and consortium blockchains are typically more efficient than public blockchains. Public blockchains can suffer from slower speeds due to the larger number of validators.
Also Read: What Is The Role Of Consortium Blockchains In Business?
Conclusion
The choice of blockchain for financial transactions depends on the specific needs of the business or individual. Public blockchains offer the highest level of decentralization and transparency, making them ideal for use cases that require global participation, like cryptocurrencies. Private blockchains provide greater control and privacy, making them suitable for businesses that want to maintain confidentiality while still benefiting from blockchain technology. Consortium blockchains strike a balance between decentralization and control, offering an ideal solution for collaborative efforts between trusted parties.
For financial transactions where security, scalability, and privacy are key concerns, consortium blockchains may offer the most balanced solution, combining the best of both worlds. However, businesses should evaluate their specific requirements and choose the blockchain that best suits their needs.